The most notable Tesla feature – apart from its electric powertrain – is its enormous touchscreen display. Since its launch, oversized in-vehicle infotainment (IVI) systems have become ubiquitous in new models, making it easier for drivers to access music, maps, and other capabilities. But that's just scratching the surface of what's possible.
Google launched Android Automotive in 2017, enabling automotive manufacturers to use a full-fledged Android OS for their IVI systems, opening the door to a much higher degree of interaction with vehicle hardware and the involvement of third-party developers.
Let's take a closer look at Android Automotive, how it compares to Android Auto, Google Automotive Services, and adoption rates.
What is Android Automotive?
Android Automotive is a variant of the Android operating system for use in vehicles, providing a stable base for manufacturers to build infotainment systems and head units. Given its extensive use in smartphones over the past decade, the platform has robust security, compatibility, developer tools, and infrastructure – plus it's free and open source.
Automotive manufacturers can heavily customize the look and feel of the operating system, creating unique infotainment experiences for their customers. The platform also opens the door to third-party developers building custom applications that can tap into automotive hardware in a variety of unique and convenient ways.
For example, using Google's voice assistant, you might say, "Hey Google, my feet are cold," and the system would automatically bump up the temperature a few degrees and redirect warm air to lower vents. The technology could also sync with smart home technologies to open garage doors, turn on lights, or set thermostats upon arrival.
Android Automotive Architecture
Many vehicle subsystems use bus topologies to connect with each other or in-vehicle infotainment (IVI) systems. Not surprisingly, the bus type and protocol vary widely between manufacturers and vehicle models. Fortunately, Android Automotive's hardware abstraction layer (HAL) provides a consistent interface regardless of the bus topology.
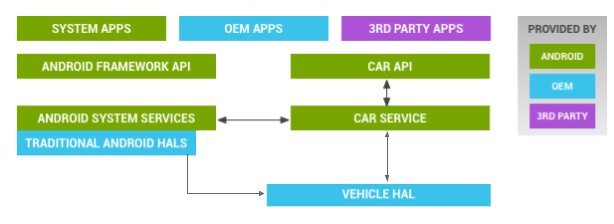
Android Automotive’s architecture simplifies development. Source: Google Android Documentation
System integrators can implement a vehicle HAL module by connecting function-specific platform HAL interfaces with technology-specific network interfaces. As a result, developers have access to a streamlined vehicle API – known as the Car API and Car Service – to access different physical subsystems, like windows, mirrors, seats, doors, or the steering wheel.
Android Auto vs. Android Automotive
Android Automotive comes after the launch of Android Auto in 2015, creating some confusion about the differences between the two.
Most people are familiar with Android Auto, which enables users to plug in their Android smartphone to compatible in-vehicle infotainment systems via a USB port or Bluetooth connection. In essence, the platform enables users to access certain Android apps on their smartphone through an existing IVI, such as Google Maps for directions.
On the other hand, Android Automotive is an entire operating system and platform that runs directly on in-vehicle hardware. It's a full-stack platform that powers the infotainment experience without a smartphone, replacing in-house IVI software and providing a platform for third-party developers to access vehicle hardware.
What is Google Automotive Services?
Google Automotive Services, or GAS, is a collection of applications and services that automotive manufacturers can choose to license and integrate into their in-vehicle infotainment systems. While manufacturers don't need them to use the operating system, they provide a jumpstart on critical functionality and are maintained by Google engineers.
Google's monetization strategy with Google Automotive Services mirrors its strategy in the mobile arena with Google Mobile Services (GMS). While Amazon Fire tablets and some other products forego GMS, most smartphone and tablet manufacturers license these apps from Google to provide a consistent user experience.
Similarly, there are some automotive manufacturers that will choose not to license GAS. For example, the UConnect 5 infotainment system uses TomTom maps and Amazon Alexa voice services instead of GMS. However, General Motors, Volvo, and other major automotive manufacturers license GAS to provide a consistent experience.
Android Automotive Adoption Trends
Automakers have already started adopting Android Automotive to power their in-vehicle infotainment systems.
General Motors includes Android Automotive on its 2022 Chevrolet Tahoe and Suburban, as well as on the luxury version of its GMC Yukon. In addition, the company is rolling out the technology on its Chevrolet Silverado and GMC Sierra pickups, along with its Hummer EV, electric SUVs, and Cadillac Lyriq electric crossover.
In addition to General Motors, Android Automotive is currently used on Ford, Polestar, and Volvo vehicles, along with Honda's upcoming 2022 line-up. And as we mentioned earlier, Stellantis's UConnect 5 is also based on Android Automotive, although it has been heavily customized and doesn't use Google Automotive Services apps.
Competition from Apple CarPlay & Linux
Android Automotive is one of the most popular in-vehicle infotainment platforms, but it's not the only game in town.
Apple announced its next-generation CarPlay software at the June 2022 WDC, featuring support for multiple displays within a vehicle and built-in controls for everything from climate to instrument clusters. The company said that the first vehicles to support the new technology will be announced in late 2023 with several committed carmakers.
At the same time, BMW, Tesla, and Toyota already use Linux-based operating systems. Projects like Automotive Grade Linux aim to provide some of the same tools as Android Automotive and CarPlay in a fully open-source software stack, providing a high level of privacy and customization to drivers and automakers.
The Bottom Line
Android Automotive is a popular in-vehicle infotainment system powered by the Android operating system. In addition, Google Automotive Services provides an optional set of applications for the platform, such as Maps and Google Assistant. However, companies can build atop the free and open-source platform without any licensing requirements.
With the launch of Apple’s new CarPlay features in late 2023, Android Automotive could start to see greater competition. There are also a handful of in-house Linux-based IVI systems and up-and-coming Linux distributions focused on vehicles.
If you're interested in building in-vehicle infotainment systems or applications that run in them, Intent can help you with everything from conceptual design to technical implementation. Our team has extensive experience with embedded systems and connected technologies, enabling us to apply unique skills and expertise to your business requirements.

Greg Cargopoulos
Marketing Lead


